The last major Windows 11 23H2 feature update was released in Fall 2023. Contrary to previous fears, Windows 10 users are not completely excluded from further development. Microsoft is also planning new features for the older operating system. Given the popularity of Windows 10, there is even speculation as to whether Microsoft could extend support beyond the planned end in October 2025.
There’s also speculation about Windows 11 24H2, which could be called Windows 12 . There have been no official announcements to date. The only thing that seems certain is that the high hardware requirements will remain. Owners of older devices will therefore not be able to install Windows 11 or 12 by official means.
But that doesn’t have to be the case: Some features that Microsoft has for the next generation of the operating system can already be implemented in Windows 10 or 11 today. In addition, some features planned for later versions can already be activated now using tricks.
Further reading: 10 obscure Windows features that will blow your mind
1. The Windows file manager and the desktop
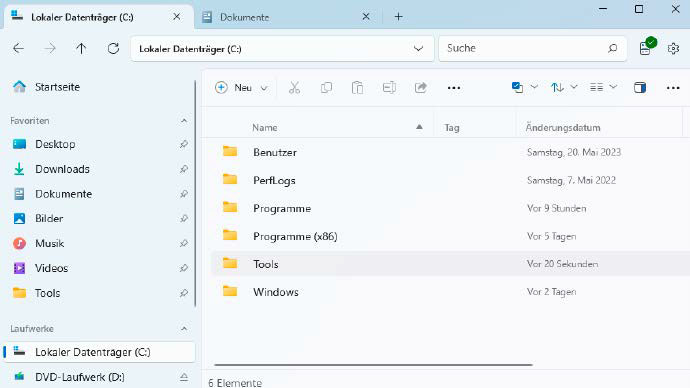
Windows Explorer clone: Files can be used in a similar way to Windows Explorer and offers useful additional functions, such as organizing files with tags.
IDG
The design of the desktop and Windows Explorer are among the areas that Microsoft is working particularly hard on. This will certainly remain the case in the future. However, changes do not only affect Windows Explorer as a stand-alone file manager. The Explorer.exe process also provides the desktop interface with icons, taskbar, and context menu. When Explorer.exe crashes, not only the file manager window disappears, but also the desktop.
However, there are plans to separate the core components of the operating system from the usable programs. Microsoft was already planning to do this with Windows 10X, but this was cancelled in 2021. The interface of this system, in particular the centered taskbar and the Start menu, were later implemented in Windows 11.
The modular structure, with a concept known as Core PC, would improve the stability of the system in the future and speed up updates. However, only Microsoft itself can achieve such a major reorganization to a Core PC.
2. Use alternative file managers for Windows
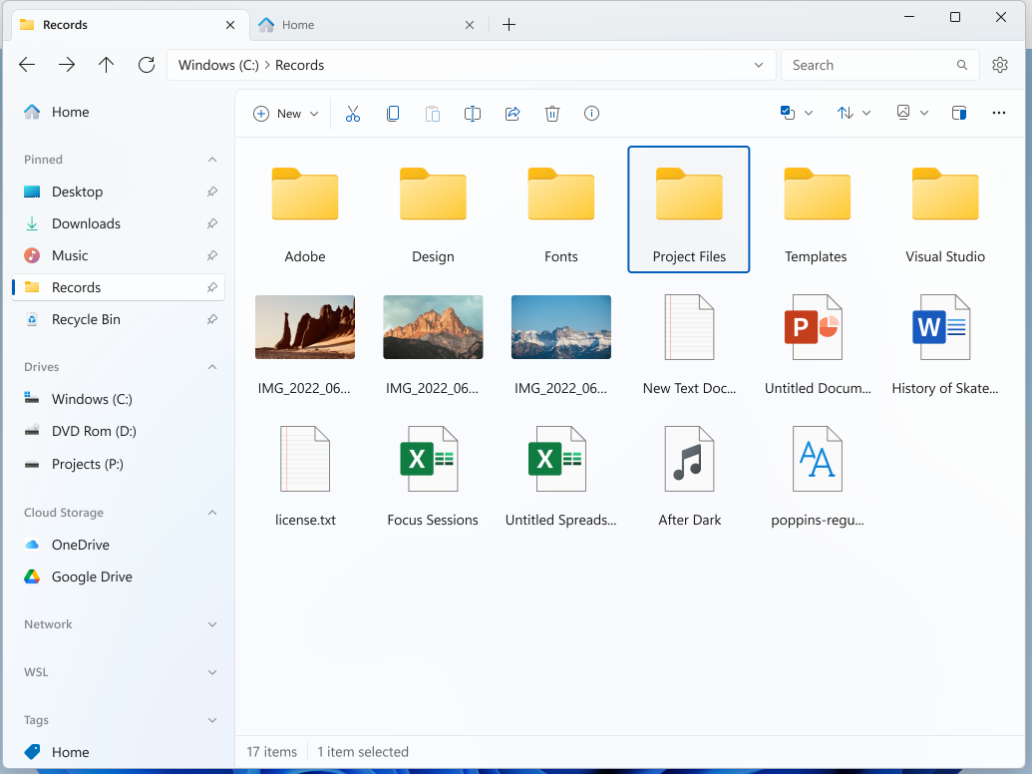
Windows Explorer clone: Files can be used in a similar way to Windows Explorer and offers useful additional functions, such as organizing files with tags.
Microsoft
If you use a different file manager, the instability of Explorer.exe can no longer affect the desktop. A modern file manager that looks similar to Windows Explorer but offers more functions goes by the name of Files.
Files can display different folders in several tabs. In the context menu of the tabs, for example, you will find the menu items “Duplicate tab” and “Open tab in new window.” A new tab can be created with the Ctrl+T key combination or via the “+” button.
If you prefer to work with a split view, you can click on “New panel” in the three-dot menu on the far right of the toolbar. This allows you to display two folders next to each other.
You can access the settings via the cogwheel symbol at the top right. Under General > Start settings you can select “Continue where you left off.” Files then remembers the open folders and restores the view the next time you start it.
Further reading: Report: Windows 12 will release in June 2024, Taiwan’s PC makers think
Dealing with archive files: Files or folders can be packed into archives in Zip and 7-Zip formats via the “Compress” context menu item. Compress > Create archive leads to a dialog in which you can specify the name and format as well as a password for the encryption. Zip, 7-Zip, and Rar archives can be opened by double-clicking, the contents viewed or files extracted.
Organize files and folders: Using the “Edit tags” context menu item, you can assign tags such as “Home” or “Work,” which Files displays in the “Tags” column. It is also possible to search for elements with tags if you prefix the search term with “tag:” In the top right-hand field. You can change the names and add new tags under “Tags” in the settings.
3. Tuning for the Windows taskbar
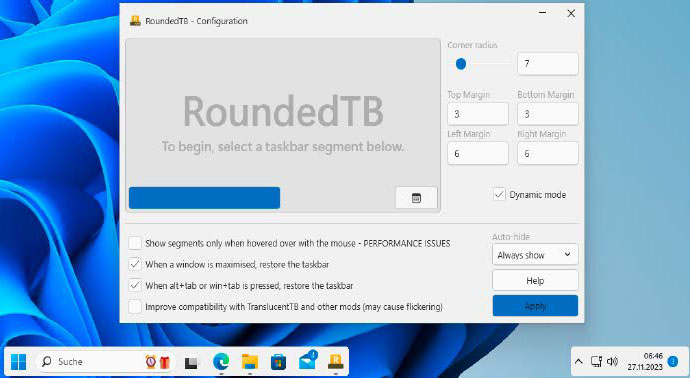
Redesign the taskbar: Rounded TB equips the taskbar with rounded corners, changes the distance to the edge of the screen and reduces the bar to the minimum required length.
IDG
The Windows interface can only be customized to a limited extent. In the “Settings” under “Personalization” you can, for example, change the design or select a different background image. There are also several options for the taskbar, some of which have been removed in Windows 11.
Many users would like a Windows taskbar that is easier to customize. It is possible that Microsoft will take these wishes into account in Windows 12. You can see a possible concept for a functional and attractively designed desktop in the following video. However, this is not an official video from Microsoft, but the art project of a Windows fan.
Until Microsoft is ready, you can also extend the design options yourself. With the free Rounded TB tool (for Windows 11), you can configure the distance between the taskbar and the edge, and you can also make the taskbar smaller. The tool is still under development. Therefore, it does not yet work completely error-free in all areas.
Once Rounded TB has been started, the distances between the taskbar and the left and right edges of the screen can be set in the window under “Left Margin” and “Right Margin.” “Top Margin” and “Bottom Margin” affect the height of the bar. Tick the “Dynamic Mode” box and click “Apply.” The free area of the taskbar disappears and it automatically enlarges depending on the number of icons.
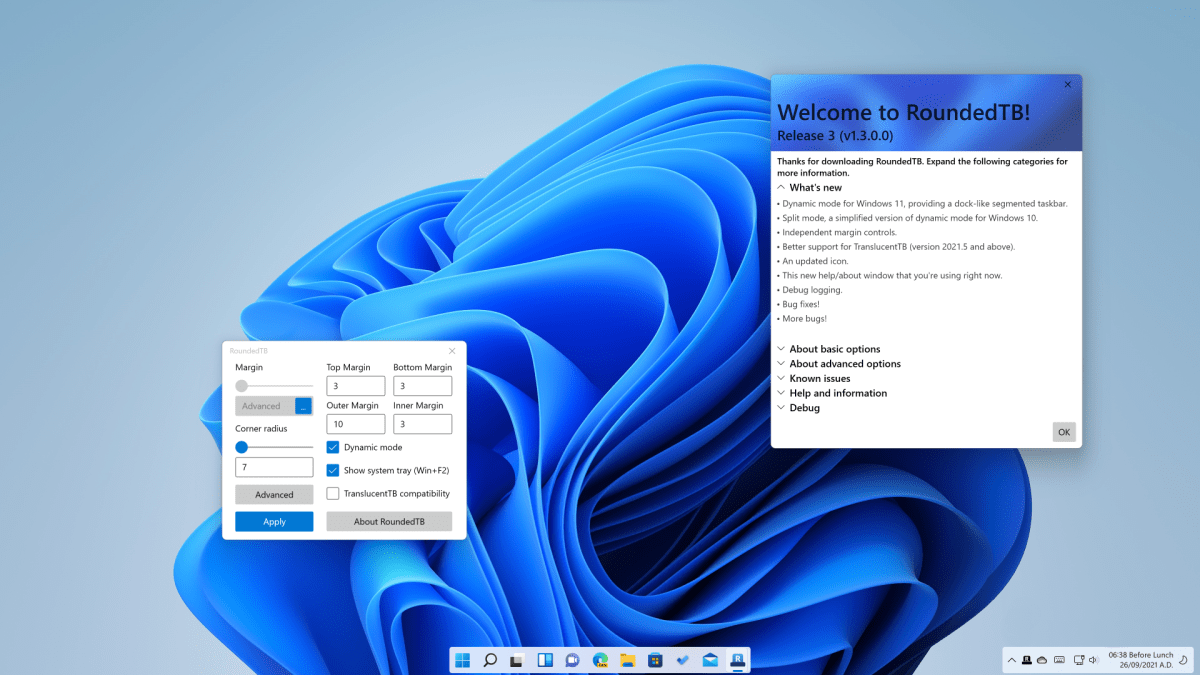
Use RoundedTB to add margins around the taskbar.
RoundedTB
The notification area appears separately on the right-hand side. If the left part of the taskbar remains visible, go to Personalization > Taskbar > Taskbar behavior in the Settings. Change the alignment from “centered” to “left-aligned” and back again. The display should then be correct.
A Mac OS-style dock: Rocket Dock is free and suitable for Windows 10 and 11. Rocket Dock displays a bar at the top of the screen with animated starter icons that lead to folders such as “Documents” or “Pictures.” Drag program shortcuts or EXE files onto the Dock to add more launchers. Using the “Dock settings,” you can specify the position on one of the screen edges, choose between different appearances and activate “Hide dock automatically” to save space on the screen.
4. Try out Windows function updates early
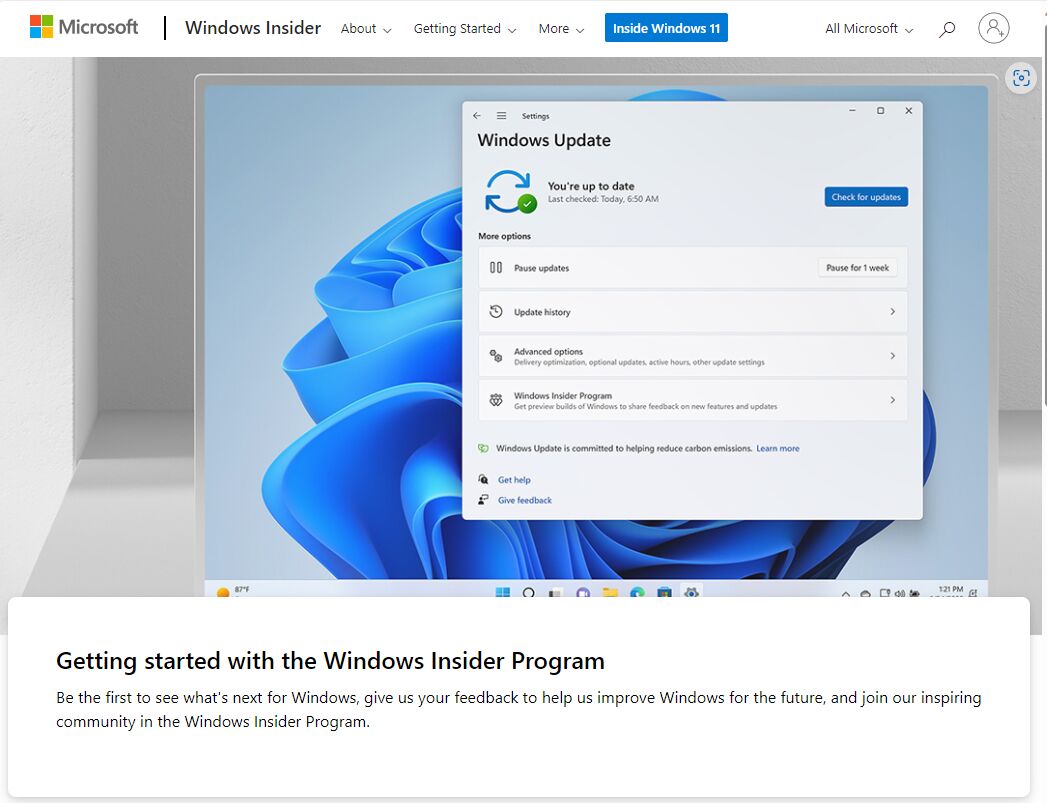
Test Windows pre-release functions: If you are curious about the latest functions, switch to the Canary Channel. You can expect the highest reliability from the Release Preview.
Microsoft
Microsoft delivers new functions to a small group of interested users first. On a production computer, you should only use the Release Preview channel. It is generally advisable to use all pre-release versions on a test computer or in a virtual machine.
If you would like to take part in the Windows Insider Program, go to Windows Update > Windows Insider Program in the Settings (Win+I) under Windows 11, click on “First steps” and follow the instructions. Registration with a Microsoft account is required. Windows 10 users go to “Windows Insider Program” under “Update & Security” and click on “Let’s go.”
New functions are delivered in waves and in different regions. It is therefore not guaranteed that your Windows will actually receive a specific feature update in advance.
If you want to find out about further developments, go to https://blogs.windows.com/windows-insider. Here you can find out which channels updates are available, what the build numbers are called, and what has changed.
Mini programs for the desktop
The widgets were popular with Windows 7 and Vista because they allowed you to put together a customized news offering. With “News and Weather,” Microsoft has once again included a widget-like option in Windows 10 (via update) and Windows 11. A short weather report can be seen in the taskbar; if you hover over it with the mouse, a window opens that also displays news or football results in addition to the weather. However, what is displayed is rather random and the display in a single window is not particularly clear.
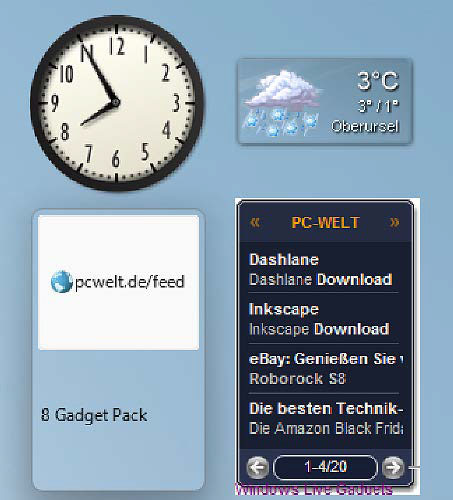
Microsoft does not offer this: 8 Gadget Pack equips Windows with small info windows that can be placed anywhere on the desktop or in a sidebar.
IDG
We don’t know whether Microsoft will continue to expand “News and Weather” and whether widgets will perhaps be able to be dragged back onto the desktop as individual windows in the future. An alternative is the 8GadgetPack. It brings the gadgets from Windows 7 back to the Windows 10 and 11 desktop.
After installation, the 8 Gadget Pack displays a sidebar with an analog clock, the Clipboarder tool for the clipboard, and the weather forecast. The individual gadgets can be configured by right-clicking and selecting “Options.” With the weather gadget, for example, you can set your place of residence.
You can drag individual gadgets with the mouse to any position on the desktop and thus detach them from the sidebar. Use the “Add gadgets” context menu to move additional gadgets to the desktop. Select the desired one by double-clicking or dragging it onto the desktop.
5. The unofficial way to the latest updates
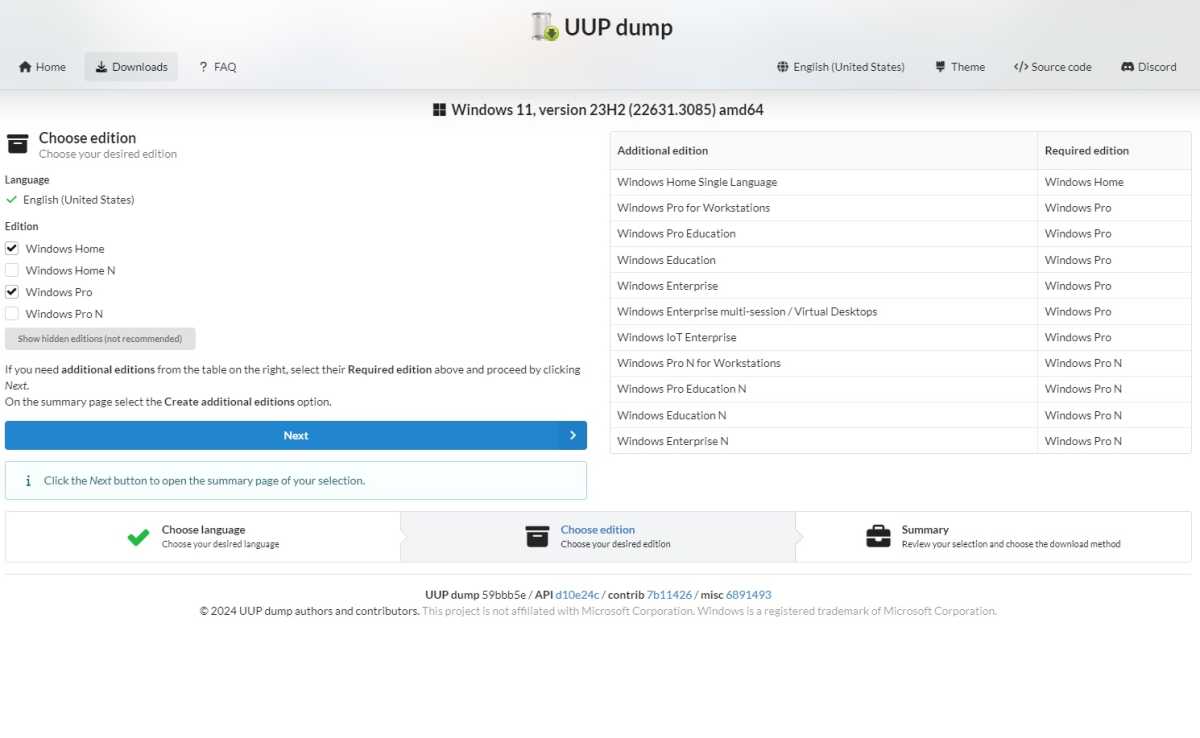
UUP Dump
The website uupdump.net always offers the latest versions from all update channels. Use the button at the top to select Windows 11 > 23H2, for example, and click on “Windows 11, version 23H2 (22631.2787) amd64” (Preview Release). Windows 10 users select Windows 10 > 22H2 and then “Feature update to Windows 10, version 22H2 (19045.3757) amd64” (Preview Release).
The version numbers are as of December 2023 and serve only as an example. The future build numbers will be different and offer other functions.
After selecting the version, set the language to “English” and click “Next.” Then tick the required edition and click on “Next.” Activate the option “Download and convert to an ISO file” and tick the box “Integrate updates if available (Windows converter only).” Then click on “Create download package” and download the ZIP file.
Unzip the downloaded ZIP file and start “uup_download_windows.cmd.” The script downloads the installation files from Microsoft servers and creates an ISO file from them.
You can use the ISO file for a new or parallel installation. A running Windows can be updated by including the ISO file in the file system in Windows Explorer via the context menu item “Deploy” and then starting “Setup.exe” from the virtual DVD drive.
6. Unlock hidden Windows features in advance
Microsoft provides Windows with new features via updates, but these are only activated from a certain date. The preview builds 22631.2787 (Windows 11) and 19045.3757 (Windows 10) mentioned above, for example, contain Windows Copilot, which enables search and Windows control via artificial intelligence (AI).
If you want to try out the functions now, you need to install the Windows versions mentioned, take part in the Insider Program and activate the new features. To do this, you will need the Vivetool, from which you should always download the latest version.
Please note: All information is a snapshot from December 2023, which is to be understood as an example. Other steps may be necessary due to updates installed in the meantime.
Step 1: Open a command prompt with administrative rights, change to the Vivetool download directory and start
vivetool.exe /enable /id:44353396Step2: Copy the file “C:WindowsSystem32IntegratedServicesRegion-PolicySet.json” to a backup folder and open it in a text editor. Search for “Windows CoPilot.”
Step 3: In the command prompt with administrative rights, change the access rights with
takeown /f "C:WindowsSystem32IntegratedServicesRegionPolicySet.json" && icacls "C:WindowsSystem32IntegratedServicesRegionPolicySet.json" /
grant Administratoren:F /c /lThen copy the previously changed json file to the folder “C:WindowsSystem32”.
Step 4: Restart Windows. With Windows 11, the Windows Copilot icon should appear in the taskbar. In our tests with Windows 10, this was not always the case. If this is also the case for you, press the Win+R key combination, type
microsoft-edge://?ux=copilot&tcp=1&source=taskbarand confirm with “OK.” For a faster start, create a shortcut with this line.
7. Use artificial intelligence without Microsoft
The innovations planned for the future at Microsoft are all about AI. Copilots will not only be available for the operating system, but also for several apps and Microsoft Office.
Everyone will have to find out for themselves how useful this is in their day-to-day work. However, not everyone is comfortable sending other personal data to Microsoft in addition to search queries.
If you want to try out an alternative, you can use GPT 4 All, for example. The program allows you to download freely available AI models and use them locally without an internet connection. The models are several GB in size and require up to 8GB RAM. Operation is similar to Bing Chat or Windows Copilot. You enter a question or task and receive an answer from the AI.
AI support can also be useful in Powershell or Command Prompt, which Microsoft is probably planning for Windows Terminal. Terminal GPT can already do this. If you ask the tool for a command line, it checks the response and can execute the line immediately. Shell GPT works in a similar way, but requires a paid API key for Chat GPT.
Lama Cleaner is an image processing tool with AI support and works with a local model. The tool is a specialist for inpainting, whereby images are edited in such a way that the viewer does not recognize the changes. You can delete unwanted objects from images and the background is reconstructed appropriately.
Lama Cleaner can be extended via plugins and can then also remove backgrounds or generate images from text descriptions. Function descriptions and examples can be found at https://github.com/Sanster/lama-cleaner.
Lama Cleaner is a Python project that we have packed into a handy package for Windows. First start “win_config.bat,” which downloads the necessary program packages and then starts the configuration in the web browser. Click on “Save configurations.” Then use “win_start.bat.” The program is operated via a graphical user interface, which you call up in the web browser via the URL http://127.0.0.1:8080.
8. Controlling the computer by voice
Speech recognition and speech output are also among the future Windows construction sites. AI can be used to significantly improve the recognition rate for controlling the PC, for example.
If you already use Amazon Alexa, you can also install the associated app on your PC via the Microsoft Store. For voice control of the PC, you also need Triggercmd and a free account at www.triggercmd.com, which is limited to one command per minute (subscription 29.95 dollars per year).
Alexa can be expanded with numerous skills, for example for smart home control. You can activate the Triggercmd skill on Amazon.
Packing and unpacking for more file formats
Packing with convenience: Peazip installs its own file manager, offers very good speed, and can handle almost all common archive formats.
Peazip
Windows Explorer can unpack ZIP files and create new archives. However, it is not particularly fast and cannot create ZIP archives with password protection. Microsoft has already incorporated some improvements in Windows 11 (23H2).
Rar, 7-Zip (7z), and Tar.gz formats can now also be unpacked via Windows Explorer. As before, only ZIP archives can be created and the working speed is still below that of other programs.
It is therefore advisable not to wait for the Microsoft update, but to install the faster 7-Zip, for example. This tool can handle most common archive formats and can also pack ZIP and 7z files with password protection. The contents of ISO and WIM files can also be extracted. During installation, 7-Zip integrates itself into the context menu of Windows Explorer, which can be used to unpack or pack files or folders.
Peazip offers roughly the same functions as 7-Zip and a similar speed. The program can be used via the Windows Explorer context menu or started directly. The Peazip interface is similar to Windows Explorer and offers some convenient functions, such as testing checksums (hash) or converting to other archive formats.
If you not only want to unpack Rar files, but also create them, use the original WinRAR. Licenses are available from $29.
This article, which originally appeared on PC-Welt, was translated from German to English.